Forest Management
Forest Management
Forest management is considered as both independent scientific branch and practical field, containing many aspects of forestry, which formulates synthetic conclusions indicating the main directions of management.
Forest management is engaged in formation of relation between nature and the man on the basis of knowledge of forest state, demand society for forest functions as well as scientific achievements and experience in solving the problems of running and organic structure of forestry.
The system of information flow of forest management services can be shown as a model:
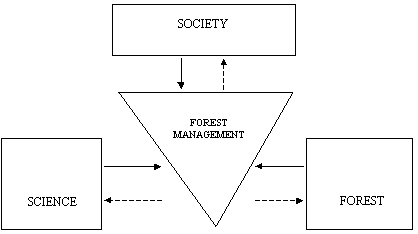
The functions of forest management can be divided as follows:
productive functions:
- increasing of the forest growing stock as a result of natural growth of trees,
- production of wood as a raw-material and consumer good available to consumption by society;
non-productive functions:
- scientific function (conduct of forest scientific research),
- protective function (protection against avalanches, floods, erosion, winds and pollution),
- landscape planning function (increasing of the forest cover by afforestation),
- climate function (effect on macro and microclimate, assimilation of carbon - CO2 - sequestration),
- tourism and recreational function,
- nature preservation function,
- function of both stimulate of economic growth and management of labor and service market.
In relation to the function mentioned above, forest management carries out the following tasks:
| Forest function | Forest management tasks | |
|---|---|---|
| Gaining information | Taking a decision | |
| The main production- increase of forest growing stock |
The inventory of forest state, measurement and calculation of the size of biomass increment, the size of forest production stock |
The calculation and choice of regeneration extent and preparation of forest regeneration plan. The preparation of forest protection plan. |
| The raw-material production -principal forest utilization |
Calculation of the size of the part of forest production stock, which can be considered as a mature to cut, checking of the changes of the sizes during the marked time period. |
The calculation and choice of final cutting extent and preparation of main cutting plan. The preparation of wood selling plan. |
| Protection against avalanches, floods, erosion, winds and pollutions | The inventory of components of flora and fauna existing in forest ecosystems. | The planning of management operations, which take into account superior protection, landscape and climate functions of forest. The indication of directions of spatial management with regard to forest function. The planning of afforestation in the range of creating of national or regional |
| Landscape planning | The mapping of forest soils and forest site types. | |
| Climate | The determination of destructive factors, affecting the forest. | |
| Tourism and recreation | The monitoring of forest resources and their conditions using geomatic techniques. | The planning of tourism and recreational forest management. |
| Nature preservation |
The inspection of the task realization pointed out in suitable plans. |
The creation of protection plans for areas, which are preserved or proposed to be preserved by different forms protection (reserves, national parks etc.). |
| Game management and fishing |
The conduct of own and charged scientific research. |
The planning of the size and regulation of population of game animals and fishing. |
| Stimulate of economic growth and management of labor and service market in local community |
Influence local labor and service market by means of employment of permanent and seasonal forest workers, and stimulate economic growth by means of supply wood manufacturing trades with raw-material (sawmills, furniture manufacture, building trade etc.) |
|
Apart from the tasks resulting from functions mentioned above, forest management contains also conduct the dialogue with the representatives of society from ecological organizations, municipalities, local communities, schools and government organizations etc.
Particularly it is expressed as:
- information of society about the status of forest and its possibilities of realization often contradictory aims (reports, brochures, educational trials, workshops, courses etc.),
- conduct activities, which popularize and spread knowledge about forestry among society and ecological activities about that at schools (e.g. competitions),
- survey of public opinion on the role , which forest should play and conduct the consultations with the representatives of ecological organizations, municipalities and government, in relation to the solving of conflicts appeared in that matter.

